Binary Tree in JS ES6
Binary Tree
A binary tree is a concept of linked data structures of nodes. Each node contains a “left” reference, a “right” reference, and a data element. The topmost node in the tree is called the root.
Using:
- Binary Trees are used to represent hierarchies
- Binary Trees provide an efficient insertion and searching
- Binary Trees are very flexible data, allowing to move subtrees around with minimum effort
Binary Tree Traversals
A traversal is a process that visits all the nodes in the tree.
Depth-first traversals O(V+E) => O(n):
- PreOrder traversal - visit the parent first and then left and right children
- InOrder traversal - visit the left child, then the parent and the right child
- PostOrder traversal - visit the left child, then the right child and then the parent
Breadth-first traversal O(V+E) => O(n):
- The level order traversal. This traversal visits nodes by levels from top to bottom and from left to right
Height-balanced binary tree
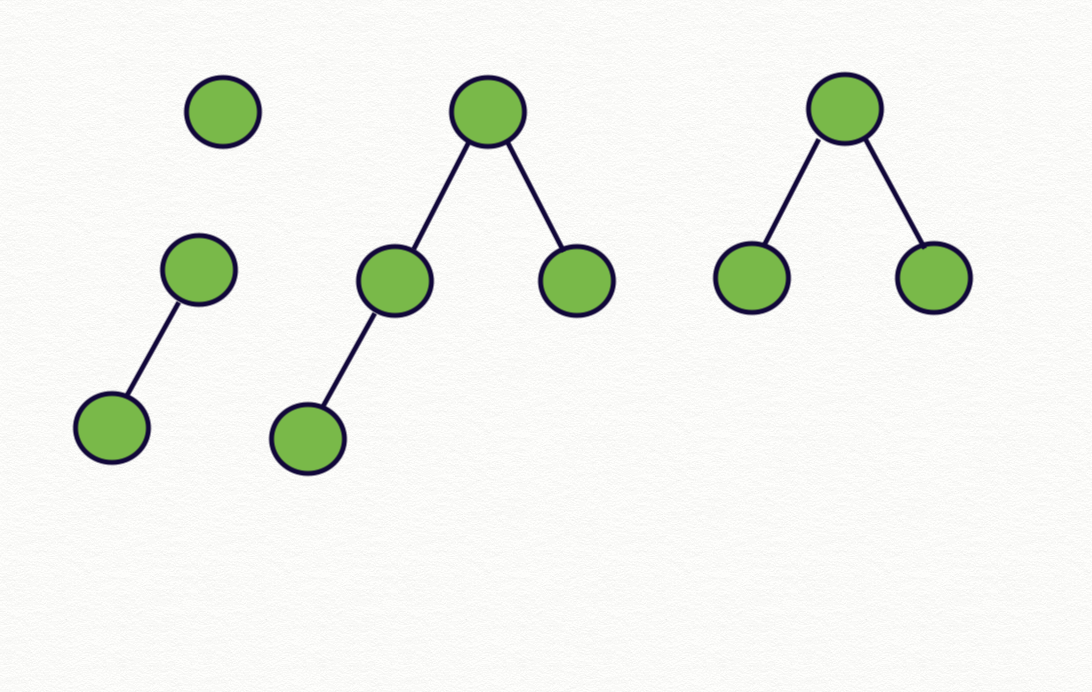
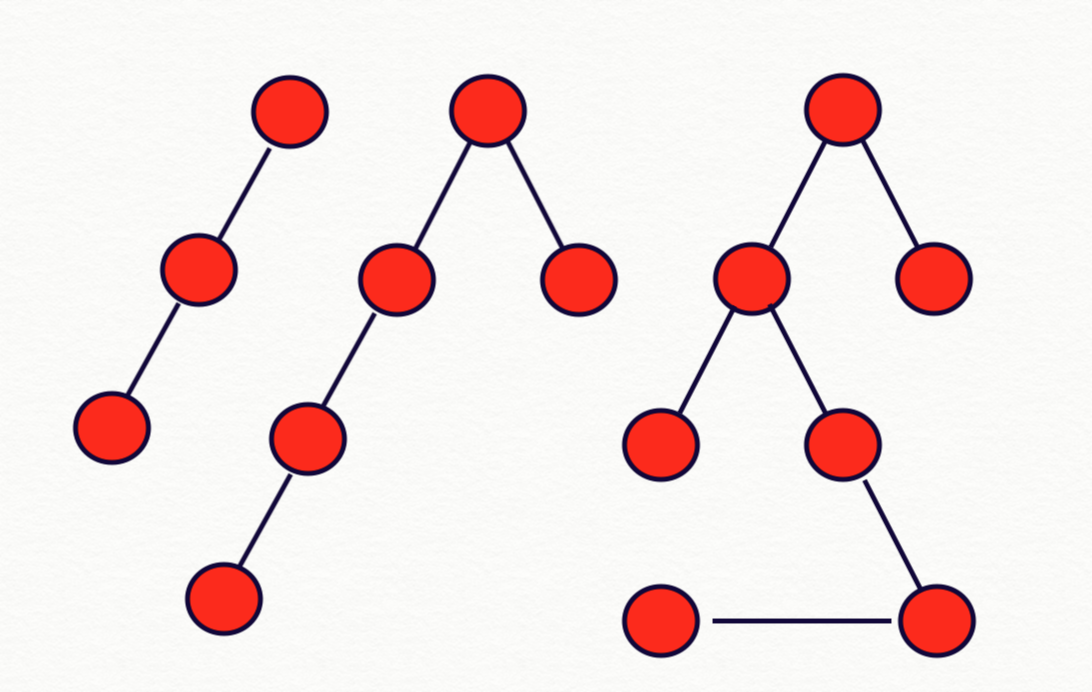 Examples balanced Binary Trees(green) and not balanced Binary Trees(red).
Examples balanced Binary Trees(green) and not balanced Binary Trees(red).
Binary tree in which the height of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than 1.
- Its left subtree is height-balanced.
- Its right subtree is height-balanced.
- The difference between heights of the left & right subtree is not greater than 1.
JS ES6 Implementation
Code structure:
- class Node
- class BinaryTree
- Insert
- Remove
- Traversal
- isBalanced
'use sctrict';
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
/**
* Implementation Binary Tree with Search, Remove, Traversal, and isBalanced
*/
class BinaryTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
/**
* @param {string|int} data
* @return {Boolean}
*/
insert(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return true;
}
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
return true;
}
/**
* @param {Node} node
* @param {Node} newNode
* @return {Boolean}
*/
insertNode(node, newNode) {
// if the data is less than the node data move left of the tree
if (newNode.data < node.data) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode;
return true;
}
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
return true;
}
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode;
return true;
}
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
return true;
}
/**
* @param {string|int} data
* @return {Node|null}
*/
remove(data) {
return this.root = this.removeNode(this.root, data);
}
/**
* @param {Node} node
* @param {string|int} key
* @return {Node|null}
*/
removeNode(node, key) {
if (node === null || (node.left === null && node.right === null)) {
return null;
}
if (key < node.data) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
}
if (key > node.data) {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
}
if (node.left === null) {
return node.right;
}
if (node.right === null) {
return node.left;
}
// Deleting node with two children
// minumum node of the rigt subtree
// is stored in aux
var aux = this.findMinNode(node.right);
node.data = aux.data;
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, aux.data);
return node;
}
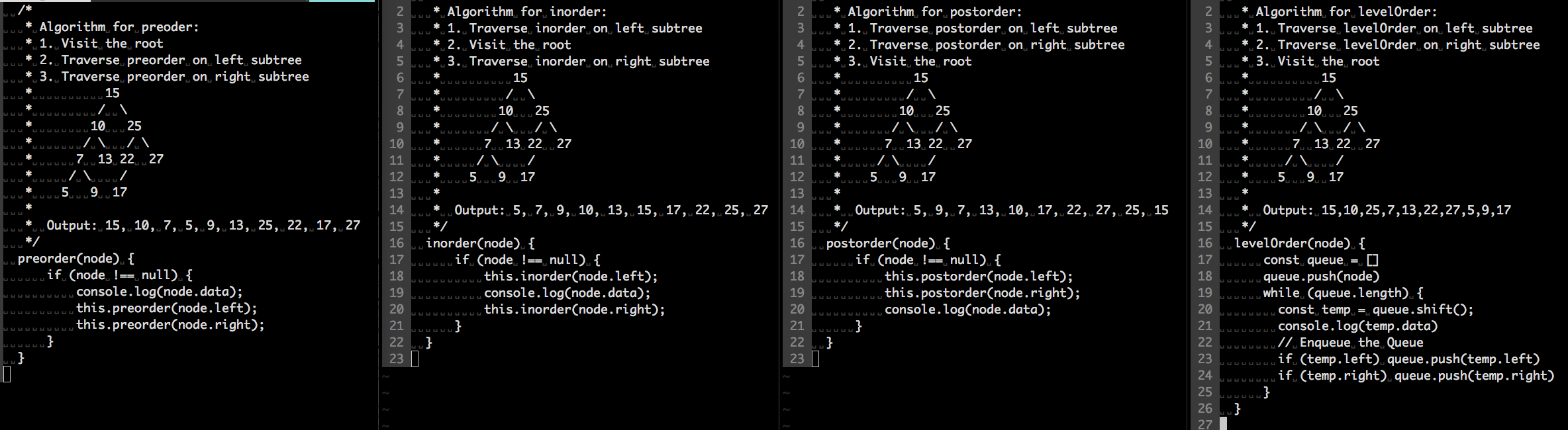
/*
* Algorithm for inorder:
* 1. Traverse inorder on left subtree
* 2. Visit the root
* 3. Traverse inorder on right subtree
* 15
* / \
* 10 25
* / \ / \
* 7 13 22 27
* / \ /
* 5 9 17
*
* Output: 5, 7, 9, 10, 13, 15, 17, 22, 25, 27
*
* @param {Node} node [description]
* @return print Node data
*/
inorder(node) {
if (node !== null) {
this.inorder(node.left);
console.log(node.data);
this.inorder(node.right);
}
}
/*
* Algorithm for preoder:
* 1. Visit the root
* 2. Traverse preorder on left subtree
* 3. Traverse preorder on right subtree
* 15
* / \
* 10 25
* / \ / \
* 7 13 22 27
* / \ /
* 5 9 17
*
* Output: 15, 10, 7, 5, 9, 13, 25, 22, 17, 27
*
* @param {Node} node [description]
* @return print Node data
*/
preorder(node) {
if (node !== null) {
console.log(node.data);
this.preorder(node.left);
this.preorder(node.right);
}
}
/*
* Algorithm for postorder:
* 1. Traverse postorder on left subtree
* 2. Traverse postorder on right subtree
* 3. Visit the root
* 15
* / \
* 10 25
* / \ / \
* 7 13 22 27
* / \ /
* 5 9 17
*
* Output: 5, 9, 7, 13, 10, 17, 22, 27, 25, 15
*
* @param {Node} node [description]
* @return print Node data
*/
postorder(node) {
if (node !== null) {
this.postorder(node.left);
this.postorder(node.right);
console.log(node.data);
}
}
/*
* Algorithm for levelOrder:
* 1. Traverse levelOrder on left subtree
* 2. Traverse levelOrder on right subtree
* 3. Visit the root
* 15
* / \
* 10 25
* / \ / \
* 7 13 22 27
* / \ /
* 5 9 17
*
* Output: 15,10,25,7,13,22,27,5,9,17
*
* @param {Node} node [description]
* @return print Node data
*/
levelOrder(node) {
const queue = [];
queue.push(node);
while (queue.length) {
const temp = queue.shift();
console.log(temp.data);
// Enqueue the Queue
if (temp.left) {
queue.push(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right) {
queue.push(temp.right);
}
}
}
/**
* @return {Node|null}
*/
getRootNode() {
return this.root;
}
/**
* @param {Node} node
* @param {string|int} data
* @return {Node|null}
*/
search(node, data) {
if (node === null) {
return null;
}
if (data < node.data) {
return this.search(node.left, data);
}
if (data > node.data) {
return this.search(node.right, data);
}
return node;
}
/**
* @param {Node}
* @return {Node}
*/
findMinNode(node) {
return node.left === null ? node : this.findMinNode(node.left);
}
/**
* @param {Node} root
* @return {Boolean}
*/
isBalanced(root) {
if (root === null || (root.right === null && root.left === null)) {
return true;
}
const dL = this.findDeep(root.left);
const dR = this.findDeep(root.right);
// An empty tree is height-balanced. A non-empty binary tree T is balanced if:
// 1) Left subtree of T is balanced
// 2) Right subtree of T is balanced
// 3) The difference between heights of left subtree and right subtree is not more than 1.
const diff = Math.abs(dL-dR) <= 1;
return diff && this.isBalanced(root.left) && this.isBalanced(root.right);
};
/**
* @param {Node} root
* @return {int}
*/
findDeep(root){
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
const deepL = 1 + this.findDeep(root.left);
const deepR = 1 + this.findDeep(root.right);
return deepL > deepR ? deepL : deepR;
}
}At the end
 Example Binary tree in nature.
Example Binary tree in nature.